If the space between the door and the frame is different at the top than it is at the bottom, you've either got a door problem, or you're going to have a door problem.
As a locksmith I was called many times to fix what the customer thought was a lock problem only to find that the problem was with the door, not with the lock. “What’s the difference?” you may well ask, proving to me that you are no locksmith. “Well,” I would smugly reply, relishing my brief moment in the spotlight of useful knowledge. “I’ll tell you.” And I will, too.
Overview
Hardware and doors age together and develop different and sometimes incompatible symptoms of aging. Like people, doors are subject to the prolonged effects of gravity. Things start to sag, and for a while you can tighten things up and slow down or even perhaps reverse the effects, but eventually Newton will have his way and what was put up will come down. That is to say the door, suspended an eighth of an inch (ideally) above the threshold, will eventually come to rest on that threshold. If left to the ravages of time it will eventually cut a groove in the threshold.
Locks, meanwhile, start having trouble finding their strikes. (A strike is to a lock what a tunnel is to a train or the side pocket to the eight ball.) Usually (but not always) the strike stays put, but the lock travels downward along with the lock side of the door. Eventually the lock may not line up with the strike at all, but before that there will be friction between the bolt or latch and the strike, making the lock difficult and eventually impossible to lock and/or unlock.
Besides sagging, wooden doors may warp and door frames of any construction may move as the building shifts and settles over time. These changes may also result in locks that no longer line up and do not work properly.
Diagnoses and Remedies
The Sagging Door
Looking at the closed door from the ‘pull’ side, it is often easy to see if it is sagging. If the jamb has not moved and was installed correctly, it is perfectly square. Ideally there will be a one eighth inch gap between the top and the left and right edges of the door and the frame. If the door hangs at an angle to the frame, it is probably sagging.

Marks on this ANSI 4-7/8 strike plate show that the latch has traveled down as it has traveled through time because of gravity.
If a door is sagging enough, there will be marks on the lock edge of the door where it is rubbing against the frame.
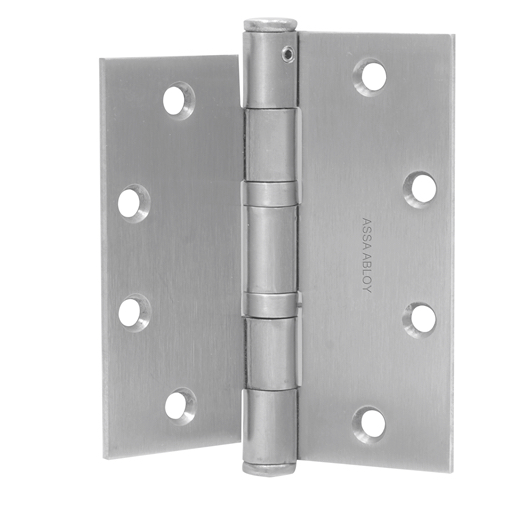
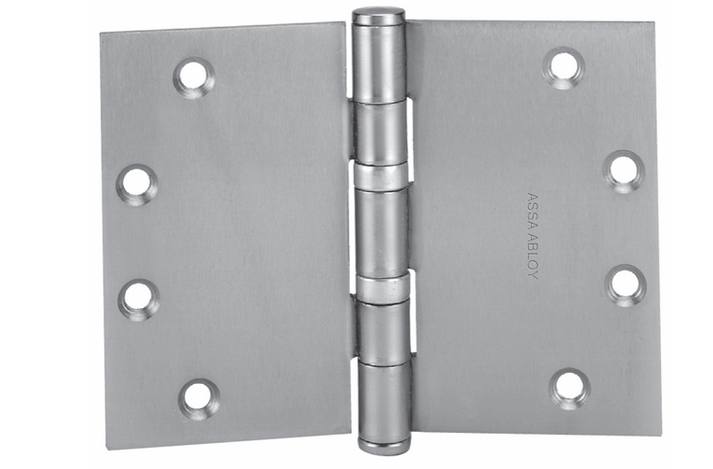
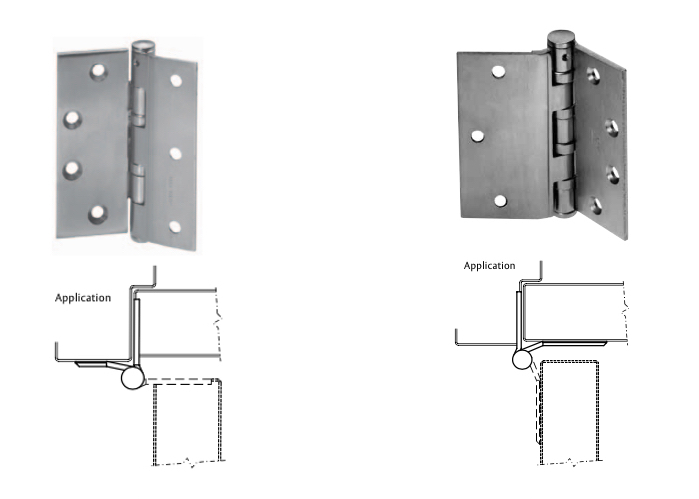
Often this is because the top hinge is loose. If you tighten all the hinge screws this may solve the problem. On a wooden door and/or frame you may find that the screws for the top hinge are stripped – that is, the screw hole has become enlarged because the weight of the door has pulled the screw out. The solution for this situation may be longer screws. Be sure you replace the screw with one of the same wire size so it fits flush in the countersunk screw hole of the hinge. Commercial hinges use a size 12 screw, but bring one of the screws to the hardware store to match it up if you have any doubts.
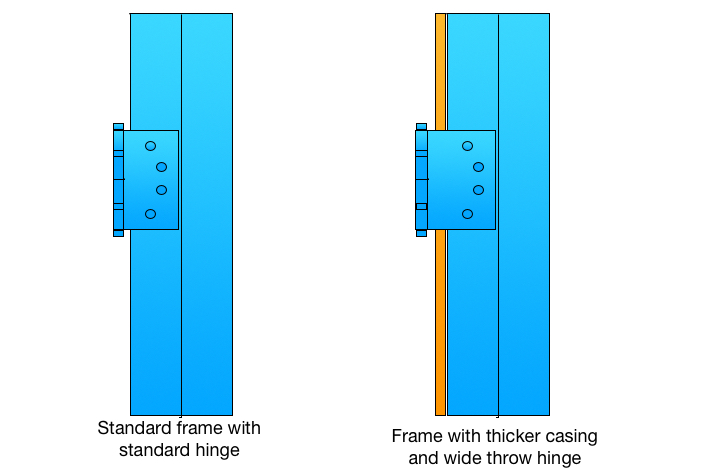
Many times longer screws do not solve the problem because the wood door is not solid would, but particle core or gypsum core, or the frame is shimmed out from the studs so far that that there is nothing for a screw less than five inches long to grab. In this case it might be necessary to relocate the top hinge (not generally a good result), install an additional hinge or hinges above and/or below the existing top hinge, install a reinforcing pivot hinge at the top of the door, or replace all the hinges with a continuous hinge.
Damaged Hinges and Crooked Door Jambs
If hinge tightening does not solve the problem, the hinge or hinges may be bent or the door frame may have shifted.
Hinges are often bent when someone (who is not too bright) places a 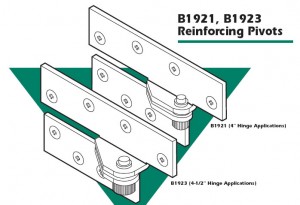 piece of wood between the door and the frame to hold the door open. It is possible to bend a hinge back to almost its original shape, but when it is bent the metal of the hinge is fatigued and it will never be the same. Since hinges vary by manufacturer, it is best to replace all the hinges if one is bent unless you can find an exact replacement for the bent hinge.
piece of wood between the door and the frame to hold the door open. It is possible to bend a hinge back to almost its original shape, but when it is bent the metal of the hinge is fatigued and it will never be the same. Since hinges vary by manufacturer, it is best to replace all the hinges if one is bent unless you can find an exact replacement for the bent hinge.
If the hinges are neither loose nor bent, the door frame may be out of alignment. Use a carpenter’s square to check the corners of the frame and a level to check the legs and header.
If it is a three-piece, knock down hollow metal frame in a sheet rock wall, you may find an adjustment screw at about eye level on each leg of the frame. These vary widely between door manufacturers, so see what kind of driver may be required to turn the adjusting screw. You can experiment with the adjusting screw to see if turning one or the other either way has any desirable effect. Sometimes the adjustment screws are not connected to anything that has contact with anything else. In that case turning the adjustment screws will have no effect.
Hollow metal frames that are installed in interior sheet rock walls are often secured to the wall at the bottom of each leg with a screw. If the floor has shifted beneath the frame so that one leg is now lower than the other, it is possible to remove the screws from both sides of the leg, gently pry the leg up off the floor a little and insert shimming material beneath the leg to hold it up.
Wooden Doors and Frames
Wooden doors and frames are generally susceptible to more movement than hollow metal. In addition to sagging, there is warping, twisting and swelling that may occur. Fortunately whenever finished wood rubs up against something, it tends to leave a mark. These marks can tell you what the door is up to and help you fix the problem.
Unlike a hollow metal or Fiberglas door, you can plane a wood door down. Careful, though: make sure you iron out any hinge problems before you start to plane, otherwise you’ll plane, the door will sag more, you’ll plane some more, the door will sag some more – pretty soon you’ll have a big space between the frame and the door someplace and you won’t need a door viewer anymore because you’ll be able to see out the crack.
One has no choice but to plane a door that has swollen. Plane carefully, a little at a time, and do your best to keep the door as square as possible. After planing, finish the door with paint, polyurethane or varnish – especially the edges – so that it doesn’t swell again so fast.
This is not a complete list of door problems, but it is a good sampling. I hope it serves as a starting point for you to solve your own.